Introduction:
Introduction of Mechanisms is very important to study in Theory of Machines for Mechanical Engineering Students.
What is machine?
The machine is a device which receives energy in some available form and utilizes it to do some particular type of work. When a mechanism or numbers of mechanisms are used to transmit the power, the mechanism is called as machine.
What is mechanism?
When one of the links of a kinematic chain is fixed, than the chain is called as mechanism. Mechanism is a part of machine which has moving parts that perform some function. It is a branch of scientific analysis which deals with motions, time and forces is known as mechanism.
The introduction to study of mechanisms can be divided as shown in figure:

Kinematics: It deals with the relative motion between various parts of the machines.
Dynamics: It deals with the forces and their effects, while acting upon the machine parts in motion.
Kinetics: It deals with the inertia forces which arise from the combine effect of the mass and motion of the machine parts.
Statics: It deals with the forces and their effects while the machine parts are at rest. The mass of the parts is assumed to be negligible.

Kinematic Link or Element:
The part of machine which has relative motion with respect to some other part of machine is called as link or kinematic link. Examples are piston, connecting rod, crank shaft, etc.
Types of links are,
- Rigid Link.
- Flexible Link.
- Fluid Link.
Kinematic Pairs:
The two links of a machine, it connects with has some relative motion. The pair is called as kinematic pair.
Types of kinematic pairs are,
- According to nature of relative motion
- Sliding Pair
- Turning Pair
- Rolling Pair
- Screw Pair
- Spherical Pair
- According to nature of contact
- Lower Pair
- Higher Pair
- According to nature of mechanical arrangement
- Open Pair
- Closed Pair
Kinematic Chain:
When a kinematic pairs are coupled in such a way that the last link is joint to the first link to transmit the motion, is called as a kinematic chain.
Types of joint in a kinematic chain,
- Binary Joint.
- Ternary Joint.
- Quaternary Joint.
Kinematic Constrained Motion:
When there is a relative motion between two links, then it is called as constraints motion. There are three types of kinematics constraints or constraints motions.
Completely Constrained Motion:
When the Motion between the link of a pair is definite direction, the motion is called as completely constraints motion. Example is piston and cylinder.

Incompletely Constrained Motion:
When motion between the link of a pair can takes place more than one direction, the motion is called as incompletely constraints motion. Example is shaft in circular hole.
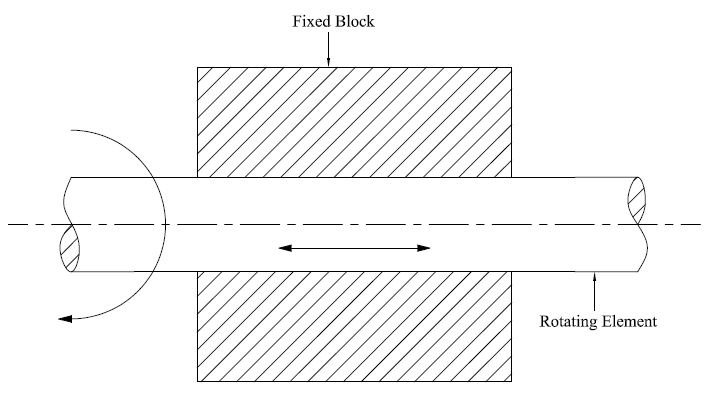
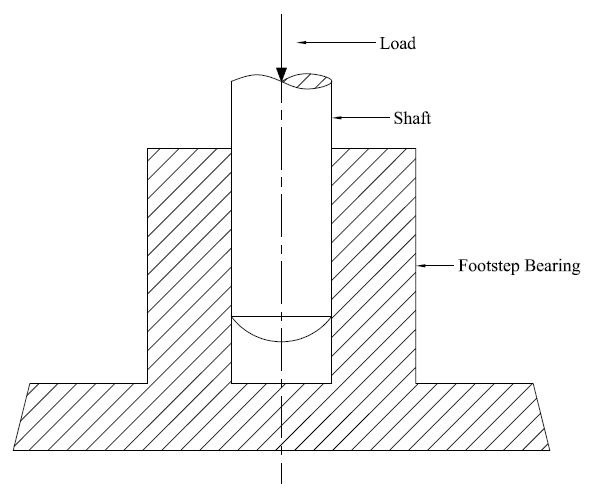
Successfully Constrained Motion:
The motion between the pair is not completed by itself but by other external agency than the motion is called as successfully constraints motion. Examples are Shaft and footstep bearing.
Comparison between Machine and Mechanism:
| Machine | Mechanism |
| When a mechanism or numbers of mechanisms are used to transmit the power, the mechanism is called as machine. | When one of the links of a kinematic chain is fixed, than the chain is called as mechanism. |
| Machine can be a combination of number of mechanisms. | Mechanism is a combination of number of kinematic links. |
| Machine is designed for transmitting motion as well as force. | Mechanism is designed for transmitting motion. |
| In the design of machine, stress and temperature are considered. | In the design of mechanism, the lengthwise dimensions are considered. |
| Examples are Lathe, Milling, Drilling, Shaper, etc. | Examples are Clock, Type writers, etc. |
Degree of Freedom:
Degree of freedom is one of the most important factors in the design or analysis of a mechanism.
“The number of independent variables that must be specified to define completely the condition of the system is called as degree of freedom”.
