Ultrasonic machining is one of the non-traditional machining processes. This is one of the types of machining process which uses less heat in the process. Ultrasonic machining process is an abrasive process which can create any material into hard and brittle form with the help of its vibrating tool. This machining process is also known as Ultrasonic impact grinding.
Working Principle of Ultrasonic Machining:
Ultrasonic machining process works on the principle that removes material from the surface of a part through high frequency, vibrations of tool against the material surface in the presence of abrasive particles.
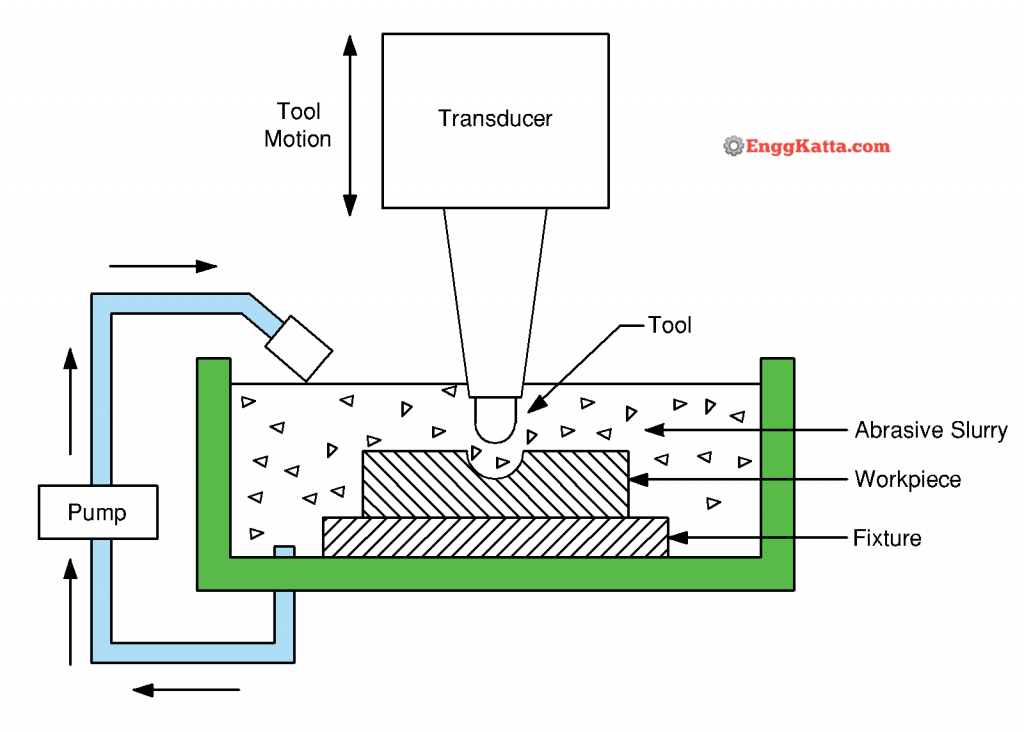
The tool travel vertically to the surface with amplitudes of 0.05 to 0.125 mm is made to oscillate in the control unit produces an alternating current oscillating at the high frequency of around 15-25 KHz in a direction normal to surface being machined. The abrasive particles are mixed with water and allow to flow as slurry between tool and work metal removal is obtained by hammering action of abrasive particles on work.
Setup of Ultrasonic Machining:
- High frequency oscillator.
- Tool Holder.
- Abrasive slurry.
Read Also: Electro Discharge Machining (EBM)
High Frequency Oscillator:
The generator acts as a power supply system and converts low frequency (60 Hz) electrical power to high frequency (20 KHz). This high frequency energy is transmitted to transducer. The transducer may be piezoelectric or magnetic resistive.
In piezoelectric transducer, if current is applied to certain materials like quartz the material increases minutely in size and all removal of current regain its original size.
The magneto resistive transducer consists of state of nickel laminations wound with a coil when high frequency current is passed through the coil changes in the electromagnetic field, produced longitudinal streams in laminations which are then part on tool holder.
Tool Holder:
Tool holder is used for holding the tool and it may be of amplifying type and non-amplifying type.
The function of tool holder is to hold the tool and transfer the mechanical energy of the tool.
Non-amplifying tool holders are cylindrical in shape and do not affect amplitude of stroke. The amplifying tool holder have modified cross section and amplified stroke and thus used high material removal rate.
The tool holder is made of aluminum, stainless steel, titanium alloy, etc. The tool is either brazed soldered or fasten mechanically of tool holder it may be of copper, brass, stainless steel, mild steel, etc.
Abrasive Slurry:
The most commonly used abrasives are aluminum oxide, boron carbide in a slurry form. The gap size ranges from 200 to 1000.
Advantages of Ultrasonic Machining:
The following are the advantages of ultrasonic machining,
- There is no heat can be generated in this machining process.
- This process is used to machine all brittle materials.
- This process produces fine finished and structured results.
- Various holes cut shapes are possible in his machining process.
- This process is economical.
- Good surface finish with high accuracy can be achieved.
Disadvantages of Ultrasonic Machining:
The following are the disadvantages of ultrasonic machining process,
- This process has low material removal rate.
- The depth of hole is limited in this process.
- High tool wear obtained in this process during operation.
- This machining process requires high level of skills top perform.
- Unnecessary large grain sizes cause defects in the process.
Applications of Ultrasonic Machining:
The following are the applications of ultrasonic machining process,
- The ultrasonic machining process is used for machining hard and brittle materials like glass, ceramic, etc.
- It is used for drilling of non-circular holes in hard metals.
- Its is used for trepanning, threading and coining.
- It is used for machining very precise shapes.
- It is used for drilling the round holes of any shape.


